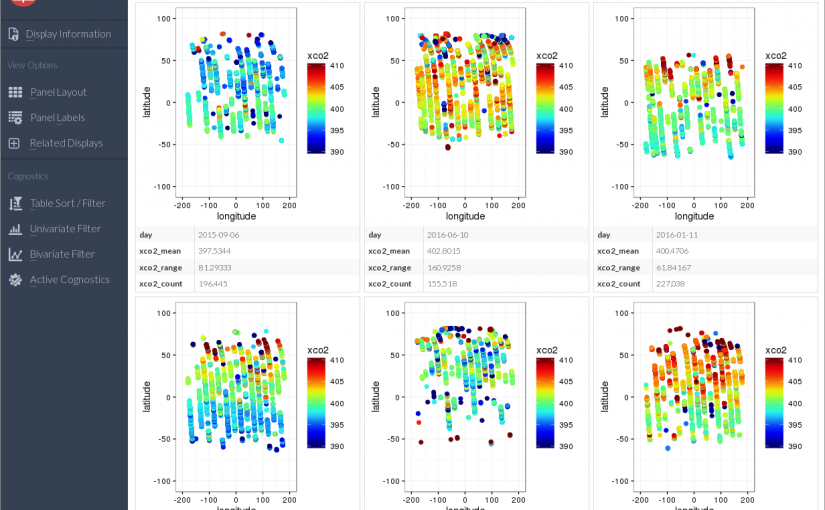
NASA JPL’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2) was launched into sun-synchronous orbit around the Earth on July 2, 2014. It carries 3 grated spectrometers for measuring the spectrum of sunlight reflected off the surface of the earth, which is used to calculate the average concentration of Carbon Dioxide in the column of atmosphere beneath the satellite (XCO2). It takes 16 days to provide full coverage of the Earth’s surface.
I am using the R packages datadr and Trelliscope from the DeltaRho project (formerly called Tessera.io) to explore and visualise the XCO2 observations from the OCO-2 Level 2 Lite version 7R data product.